From Spin to Spark: Unpacking Torque and Voltage in Your DIY Generator
Motor to Generator Conversion: Decoding the Real Relationship Between Input Torque and Output Voltage
Unpacking the Hand Crank Generator Mystery: Why RPM Matters More Than Raw Strength
Every gadget enthusiast eventually encounters the fascinating mechanical flip: converting a standard electric motor into an emergency power source—a generator. This transition from consumer component to critical supply opens up a world of resilience, supporting everything from essential battery charging to innovative renewable energy experiments.
For a detailed breakdown of components and setup, check out our companion guide: Hand Crank Generators: Your Guide to a Reliable Power Source.
The central and most critical question for every DIY builder is this: If you apply serious rotational force (high torque) to the crank, does that rotational effort directly translate into a higher voltage output?
Let's dive into the core physics principles and clearly define how mechanical input becomes stable electrical output.
---Voltage Generation Factors: The Absolute Authority of Rotational Speed (RPM)
The operation of any generator rests entirely on the principle of electromagnetic induction. In basic terms, when the wire coils (the armature) move through a permanent magnetic field, a voltage is created, known as the Electromotive Force (EMF).
The magnitude of the voltage produced is directly dependent on the rate of change of the magnetic flux. This means voltage is governed by two variables, irrespective of the torque applied:
- Rotational Speed (RPM): The faster the generator spins, the quicker the magnetic field lines are cut, resulting in a significantly higher induced voltage.
- Magnetic Field Strength: A stronger magnet (common in permanent magnet motors) will increase the voltage output at any given RPM.
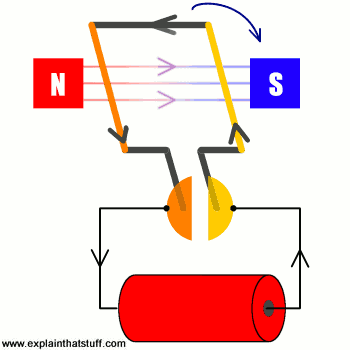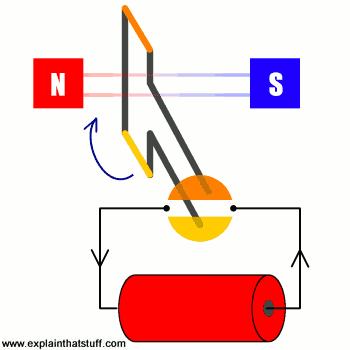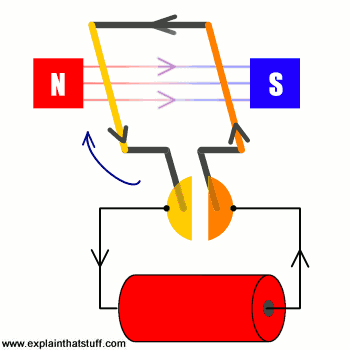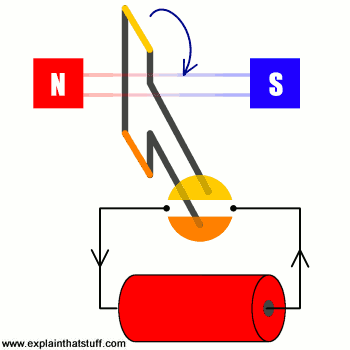
Key Takeaway: Voltage is a function of speed, not raw cranking force.
---Torque and the Generator: Sustaining Current Against Counter-Force
If rotational speed dictates voltage, then where does torque—the rotational force you apply—come into play? Torque is the mechanical effort required to start the spin and, more importantly, to keep it going efficiently when the generator is under load.
Why High Torque is Necessary for Maximum Power Output (Watts)
Torque is the essential ingredient for managing current (Amperage) and overall power (Watts = Volts x Amps). Its necessity arises from Lenz's Law:
- Enabling High RPM: You must apply torque to initially overcome the mechanical friction and inertia needed to achieve the target high RPM.
- Fighting Counter-Torque: When you plug in a device (the load), the resulting electrical current generates a secondary magnetic field. This field creates a powerful opposing force—the counter-torque—that resists the rotation. This is why turning the crank becomes noticeably harder when you connect a light bulb or charger.
- Delivering Current: To maintain the desired, stable voltage (by keeping RPM constant) while the load demands power, you must apply enough input torque to continuously overcome that counter-torque. The heavier the electrical load (the more current it draws), the higher the counter-torque, and the more input torque is required.
Key Takeaway: High torque allows you to produce the current needed to power devices by fighting the internal resistance (counter-torque) created by that current, all while preserving the high voltage set by the RPM.
---Optimizing Your Hand Crank Design: The Critical Role of Gearing
The goal of any effective DIY generator is to translate low human input torque and RPM into the high RPM required by the motor-turned-generator. This is achieved through the gear ratio.
Gearing for Voltage and Power
A high gear ratio (e.g., 50:1) means that one turn of your input handle results in 50 turns of the motor shaft. This design effectively converts your high, slow input torque into the low, fast RPM required by the generator. By correctly engineering this mechanical advantage, you can:
- Achieve High Voltage: Maximize the motor RPM to quickly hit the required voltage for charging batteries or running small devices.
- Manage Fatigue: While you still feel the counter-torque when you plug in a load, the mechanical advantage of the gearing makes it manageable, allowing you to sustain the necessary rotational speed for longer periods.
Understanding this balance is crucial for all DIY power projects. Whether you're harnessing human effort, wind power, or water flow, balancing the input force (torque) with the resulting speed (voltage) is key to a reliable, stable power supply.
---Explore Related STEM Simulators and Resources
Use the controls below to browse various STEM-related projects, simulators, and educational links directly within the viewer, or click on the optimized links for direct access.
Direct Access: Affiliate Offers and Simulation Tools
- Read: The Transformative Role of Online Education in STEM
- Affiliate Offer: Lazada STEM Kits and Components
- Collshp: Explore Comprehensive STEAM Education Resources
- Visit the Official STEM Simulator Projects Blog
- DIY Project: Wooden Solar Wind Turbine Model Kit (TikTok Shop)
- Affiliate Offer: Hand Crank Components and Parts (AliExpress)
- Affiliate Offer: Amazon Recommended Electronics Tools
- Enroll: Free Certificate Courses in Technology and Science (Alison)
- Simulator: Hand Crank Generator Energy Dynamics
- Simulator: Visualize Electromagnetic Induction Principles
- Simulator: See the Motor to Generator Conversion in Action
Join the DIY Power Discussion!
What are your experiences with converting motors into generators? Have you experimented with different gearing ratios, and what was your most successful voltage/power combination? Share your insights and questions in the comments below!







Thanks for the info
ReplyDeleteYou explained it better than my lecturer
ReplyDeleteContent worth reading
ReplyDeleteExactly what I'm looking for
ReplyDeletevery educative
ReplyDeleteI once did this accidentally while repairing a motor on a Tamiya car.
ReplyDeletethis is what I looking for... very helpful
ReplyDeletewhile torque doesn’t directly increase voltage, it enables higher rotational speeds—key to boosting voltage via electromagnetic induction
ReplyDeletemaintaining consistent rotational speed under load and achieving higher speeds, which then increase the induced voltage
ReplyDeletetorque enables the generator to spin effectively, and the speed of that spin primarily determines the voltage output
ReplyDelete